Understanding the Environmental Impact
As we navigate the challenges of a rapidly changing world, it is crucial to address the environmental impact of our actions.
One key aspect of this is the concept of life cycle analysis and carbon footprint. By examining the entire life cycle of a product or service, we can gain valuable insights into its environmental implications and make informed decisions to reduce our carbon footprint.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of life cycle analysis and carbon footprint, exploring how they contribute to sustainable growth measures and corporate sustainability. Let’s embark on this journey to uncover the hidden environmental dimensions of our choices.
The Importance of Understanding the Environmental Impact
In today’s society, where environmental concerns are at the forefront, it is essential to recognize the impact of our choices on the planet. Each decision we make, from the products we consume to the services we utilize, has far-reaching consequences. By comprehending the environmental impact, we can take proactive steps towards a more sustainable future. Life cycle analysis and carbon footprint analysis serve as powerful tools in this endeavor, enabling us to assess the environmental implications of our actions accurately.
Introducing Life Cycle Analysis and Carbon Footprint
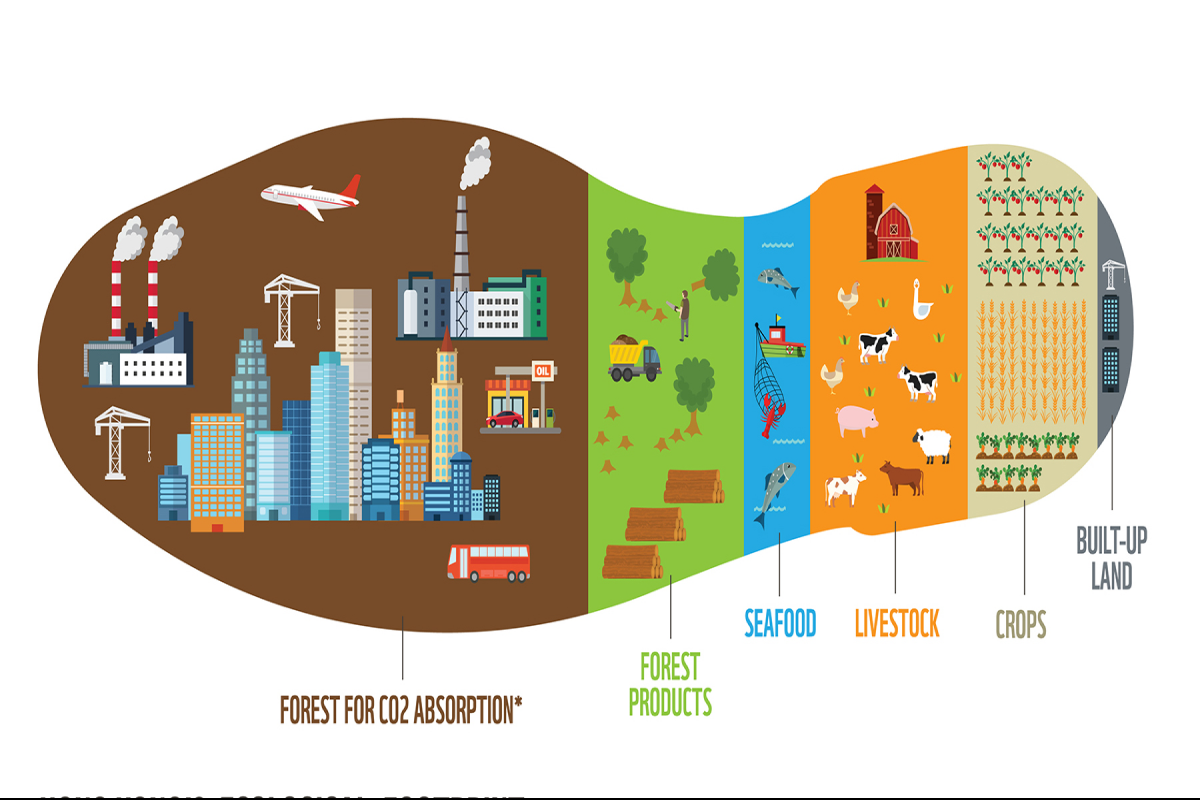
Life cycle analysis (LCA) is a comprehensive approach that evaluates the environmental impact of a product or service throughout its entire life cycle. This encompasses every stage, from the extraction of raw materials to manufacturing, distribution, use, and disposal. LCA provides a holistic perspective, considering various environmental factors such as energy consumption, resource depletion, and emissions.
Carbon footprint analysis is a specific aspect of life cycle analysis that focuses on measuring the greenhouse gas emissions associated with an individual, organization, or product. It quantifies the carbon dioxide equivalents released into the atmosphere as a result of activities and processes. By understanding our carbon footprint, we can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce emissions.
The Link to Sustainable Growth Measures
Sustainable growth measures are vital for companies to ensure long-term profitability and success. Organizations that embrace sustainable practices not only contribute to environmental preservation but also enhance their reputation and attract investors. Corporate sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting are becoming increasingly important for companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable growth. Through comprehensive assessments like life cycle analysis and carbon footprint analysis, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and align their operations with sustainable development goals.
Now that we have set the stage, let’s dive deeper into the world of life cycle analysis and carbon footprint analysis to uncover their significance and implications for a greener future.
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA)
Life cycle analysis (LCA) is a powerful tool that offers a comprehensive understanding of the environmental impact of a product or service throughout its entire life cycle. By examining each stage, from raw material extraction to disposal, LCA provides valuable insights into resource consumption, energy use, emissions, and waste generation. Let’s explore the key aspects of life cycle analysis and its significance in assessing sustainability.
Definition and Purpose of LCA
Life cycle analysis, also known as life cycle assessment, is a systematic evaluation of the environmental impacts associated with a product or service. It takes into account all stages, including raw material acquisition, production, distribution, use, and end-of-life disposal. The primary purpose of LCA is to quantify the environmental burdens and identify areas where improvements can be made to reduce the overall impact.
LCA considers a wide range of factors, including energy consumption, water usage, emissions of greenhouse gases and pollutants, waste generation, and even potential impacts on human health and ecosystems. By analyzing the complete life cycle, LCA provides a holistic view, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions based on environmental considerations.
Measuring Environmental Impact
LCA involves a thorough assessment of various environmental indicators related to a product or service. These indicators encompass different phases:
- Raw Material Acquisition: This stage involves evaluating the environmental impact of acquiring raw materials, such as mining, logging, or agriculture. It considers factors like energy consumption, land use, water usage, and associated emissions.
- Production: The production phase assesses the energy consumption, emissions, and waste generated during the manufacturing process. It takes into account factors like energy sources, manufacturing techniques, and material efficiency.
- Distribution and Transportation: In this stage, the environmental impact of transporting the product from the manufacturer to the consumer is analyzed. Factors such as transportation mode, distance traveled, packaging, and fuel consumption are considered.
- Use and Operation: This phase focuses on evaluating the environmental impact during the product’s use or operation. It includes factors like energy consumption, water usage, emissions, and waste generation resulting from user activities.
- End-of-Life Disposal: The final stage examines the environmental impact associated with the disposal or recycling of the product. Factors considered include waste management practices, emissions from incineration or landfill, and the potential for recycling or reusing materials.
Impact on Decision-Making and Sustainability Initiatives
Life cycle analysis is a valuable decision-making tool for individuals, organizations, and policymakers. By quantifying the environmental impact at each stage, LCA helps identify areas where interventions can lead to significant sustainability improvements. It enables stakeholders to make informed choices, such as selecting environmentally friendly materials, optimizing production processes, improving energy efficiency, or implementing effective waste management strategies.
LCA also plays a pivotal role in supporting sustainability initiatives and policies. Governments and regulatory bodies can utilize LCA data to develop regulations, set environmental standards, and incentivize eco-friendly practices. For businesses, LCA offers insights into supply chain sustainability, product design, and marketing strategies that align with environmental goals.
With a solid understanding of LCA, we can now delve into the specific analysis of carbon footprints, which focuses on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product or service. Let’s explore this aspect further in the next section.
Carbon Footprint Analysis: Measuring Environmental Impact
Carbon footprint analysis is a specific aspect of life cycle analysis that focuses on measuring the greenhouse gas emissions associated with an individual, organization, or product. It quantifies the carbon dioxide equivalents released into the atmosphere as a result of activities and processes. By understanding our carbon footprint, we can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce emissions. Let’s delve deeper into the world of carbon footprint analysis and its significance in environmental assessment.
Understanding Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint of an entity represents the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), released as a result of its actions or operations. This includes direct emissions from burning fossil fuels and indirect emissions from the consumption of electricity, transportation, and other activities.
Carbon footprint analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation of emissions throughout the life cycle of a product or service. It considers all stages, from raw material extraction to disposal, including production, transportation, use, and end-of-life. By quantifying the emissions associated with each stage, carbon footprint analysis enables us to gain insights into the environmental impact of our choices.
Importance of Carbon Footprint Analysis
Carbon footprint analysis is crucial for several reasons:
Addressing Climate Change
One of the primary reasons for conducting carbon footprint analysis is to address climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions contribute to global warming and climate instability. By understanding the carbon footprint, we can identify high-emission activities or products and take steps to mitigate their impact. This includes adopting cleaner energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices.
Promoting Sustainability and Responsible Consumption
Carbon footprint analysis plays a significant role in promoting sustainability and responsible consumption. By evaluating the emissions associated with products and services, consumers can make informed choices and support environmentally friendly options. It also encourages businesses to reduce their carbon footprint by adopting sustainable practices, optimizing their supply chains, and developing eco-friendly products.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly implementing regulations and standards to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon footprint analysis helps organizations comply with these regulations and meet sustainability targets. By understanding their emissions profile, businesses can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to achieve emission reduction goals.
Conducting Carbon Footprint Analysis
Carbon footprint analysis involves the following key steps:
- Defining the Scope: Determine the boundaries and scope of the analysis. This includes identifying the system boundaries, such as which stages of the life cycle to include, and the emissions sources to consider.
- Data Collection: Gather relevant data on energy consumption, material usage, transportation, and other activities contributing to emissions. This may involve collecting data from internal sources, suppliers, or industry databases.
- Calculating Emissions: Use established methodologies and emission factors to calculate greenhouse gas emissions from each activity or stage. This may include CO2, methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and other greenhouse gases.
- Interpreting Results: Analyze the calculated emissions and interpret the findings. Identify hotspots or areas with significant emissions and prioritize actions for emission reduction.
- Implementing Reduction Strategies: Develop and implement strategies to reduce emissions based on the analysis
Corporate Sustainability and ESG Reporting: Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
Corporate sustainability and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting are gaining increasing importance in today’s business landscape. Companies are recognizing the need to address environmental and social impacts while maintaining long-term profitability and success. In this section, we will explore the significance of corporate sustainability and ESG reporting, and how it contributes to enhancing transparency and accountability.
Understanding Corporate Sustainability
Corporate sustainability refers to a company’s commitment to conducting business in an environmentally and socially responsible manner. It involves integrating sustainable practices into various aspects of operations, supply chains, and decision-making processes. By considering the environmental and social impacts of business activities, companies can contribute to a more sustainable future while ensuring their own long-term viability.
The Importance of ESG Reporting
ESG reporting refers to the disclosure of a company’s performance on environmental, social, and governance factors. It provides stakeholders, including investors, employees, customers, and the public, with valuable information about a company’s sustainability efforts and impacts.
Attracting Investors
ESG reporting has become increasingly important for companies to attract investors and maintain a positive reputation. Investors are now considering environmental and social factors alongside financial performance when making investment decisions. By providing transparent and comprehensive ESG reports, companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices and appeal to investors who prioritize responsible investments.
Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
ESG reporting enhances transparency and accountability by providing stakeholders with information about a company’s sustainability performance. It allows investors, customers, and the public to evaluate a company’s environmental and social impacts, as well as its governance practices. Through ESG reporting, companies demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices and hold themselves accountable to their stakeholders.
Identifying Risks and Opportunities
ESG reporting helps companies identify risks and opportunities associated with environmental and social factors. By evaluating their performance in areas such as carbon emissions, resource usage, labor practices, diversity and inclusion, and board composition, companies can identify areas for improvement and capitalize on emerging sustainability trends.
Driving Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Corporate sustainability and ESG reporting can drive innovation and provide a competitive advantage. By integrating sustainable practices and considering the environmental and social impacts of their operations, companies can develop new products, services, and business models that meet the evolving needs of consumers and society. This positions them as leaders in sustainability and gives them a competitive
Product Carbon Footprints and Life Cycle Assessments: Evaluating Environmental Impact
Product Carbon Footprints (PCF) and Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) are essential tools for evaluating the environmental impact of products. They provide valuable insights into the resource consumption, emissions, and overall sustainability performance of a product throughout its life cycle. In this section, we will delve into the details of PCF and LCA, and their significance in assessing the environmental impact of products.
Understanding Product Carbon Footprints (PCF)
Product Carbon Footprints (PCF) focus specifically on measuring the greenhouse gas emissions associated with a product’s life cycle.
Conducting Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) And Carbon Footprint Management
Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) are comprehensive evaluations of the environmental impact of a product throughout its entire life cycle. LCA considers a broader range of environmental factors beyond just carbon emissions. It takes into account resource consumption, energy use, water usage, waste generation, and other potential environmental impacts.
Scope and Boundaries
When conducting an LCA, it is important to define the scope and boundaries of the assessment. This involves identifying which stages of the product’s life cycle to include, such as raw material extraction, production, transportation, use, and end-of-life. Determining the system boundaries ensures a comprehensive assessment that captures all relevant environmental impacts.
Life Cycle Inventory (LCI)
The Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) phase involves gathering data on the inputs and outputs of each stage in the product’s life cycle. This includes the energy and materials consumed, emissions released, and waste generated. LCI data provides a foundation for further analysis and enables comparisons between different products or processes.
Impact Assessment
In the impact assessment phase, the gathered LCI data is evaluated to assess the potential environmental impacts, such as Climate Change. This involves considering the emissions, resource consumption, and other factors identified during the life cycle inventory. Impact assessment methodologies help quantify the effects on climate change, resource depletion, human health, and ecosystems.
Interpretation and Improvement
The final phase of LCA involves interpreting the results and using them to drive improvements and inform decision-making. By analyzing the environmental impacts identified in the assessment, companies can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to reduce the overall impact of their products. This may involve optimizing processes, adopting cleaner technologies, or redesigning products to minimize resource consumption and emissions.
Benefits
The Power of Life Cycle Analysis: Driving Sustainable Practices
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) is a powerful tool that enables companies to evaluate the environmental impact of their products and make informed decisions to drive sustainable practices. By considering the entire life cycle of a product, from raw material extraction to disposal, LCA provides a holistic view of its environmental footprint. In this section, we will explore the benefits and applications of LCA in driving sustainable practices.
Understanding the Benefits of Life Cycle Analysis
Life Cycle Analysis offers several benefits for companies committed to sustainability:
Holistic Environmental Assessment
LCA provides a comprehensive and holistic assessment of a product’s environmental impact. It considers a wide range of factors, including resource consumption, energy use, emissions, waste generation, and other potential environmental impacts. This holistic approach allows companies to identify hotspots and prioritize actions for reducing their overall environmental footprint.
Informed Decision-Making
By understanding the environmental impacts of different stages in a product’s life cycle, LCA enables companies to make informed decisions. These decisions may include selecting more sustainable materials, optimizing manufacturing processes, improving energy efficiency, or implementing recycling programs. LCA provides valuable insights that support decision-making aligned with sustainability goals.
Identification of Improvement Opportunities
LCA helps companies identify improvement opportunities throughout the life cycle of a product. By analyzing the data gathered during the assessment, companies can identify areas where changes can be made to reduce environmental impacts. This may involve exploring alternative materials, optimizing transportation methods, or implementing circular economy practices.
Environmental Performance Communication
LCA provides companies with credible data to communicate their environmental performance to stakeholders. By quantifying the environmental impacts of products using standardized methodologies, companies can transparently communicate their sustainability efforts. This helps build trust with customers, investors, and other stakeholders who are increasingly interested in the environmental performance of the products they consume or invest in.
Applications of Life Cycle Analysis
Life Cycle Analysis has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are a few examples:
Product Design and Development
LCA can be used during the product design and development phase to identify opportunities for reducing environmental impacts. By considering different design options, materials, and manufacturing processes, companies can optimize the sustainability of their products from the early stages. LCA helps uncover potential environmental trade-offs and supports the development of greener and more sustainable products.
Supply Chain Optimization
LCA can be applied to optimize supply chains and reduce environmental impacts throughout the entire value chain. By assessing the environmental performance of suppliers and evaluating transportation methods, companies can make more sustainable choices. Supply chain optimization based on LCA findings can lead to reduced emissions, minimized waste generation, and improved resource efficiency.
Eco-Labeling and Environmental Certification
LCA can serve as the basis for eco-labeling and environmental certification programs, such as a carbon neutral product label. By quantifying the environmental impacts of a product, companies can provide accurate and transparent information to consumers. Eco-labels and certifications help consumers make environmentally conscious purchasing decisions and promote sustainable choices in the market.
Policy Development and Regulation Compliance
LCA plays a crucial role in policy development and compliance with environmental regulations. Governments and regulatory bodies can use LCA data to develop policies that promote sustainability and set environmental standards for industries. Companies can utilize LCA to ensure compliance with regulations and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices.
Realizing Sustainability through Life Cycle Analysis
Life Cycle Analysis empowers companies to embrace sustainability by providing a comprehensive understanding of the environmental impacts associated with their products. By leveraging the insights gained from LCA, companies can make informed decisions, drive innovation, and continuously improve their environmental performance. Incorporating LCA into business practices enables organizations to move towards a more sustainable future.
Life Cycle Analysis and Carbon Footprint Analysis: A Sustainable Future
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and Carbon Footprint Analysis are powerful tools for assessing and reducing the environmental impact of products and processes. By understanding the life cycle of a product and measuring its carbon emissions, companies can make informed decisions to create a more sustainable future.
The Significance of Carbon Footprint Analysis
Carbon footprint analysis allows companies to measure the amount of greenhouse gas emissions produced by an individual, organization, or product. It quantifies the carbon dioxide equivalents released into the atmosphere as a result of activities, providing valuable insights into the environmental impact. By conducting carbon footprint analysis, companies can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce emissions.
Conducting Life Cycle Analysis (LCA)
Life Cycle Analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation of the environmental impact of a product throughout its entire life cycle. LCA considers various stages, including raw material extraction, production, transportation, use, and end-of-life. By conducting LCA, companies gain a holistic understanding of the environmental hotspots and can identify opportunities for improvement.
Evaluating Resource Consumption
LCA helps evaluate the resource consumption associated with a product throughout its life cycle. This includes energy usage, water consumption, and material inputs. By identifying areas of high resource consumption, companies can implement measures to optimize resource efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Assessing Emissions and Waste Generation
LCA allows companies to assess the emissions and waste generated throughout a product’s life cycle. This includes greenhouse gas emissions, air pollutants, and waste streams. By quantifying these impacts, companies can develop strategies to minimize emissions, improve waste management, and reduce their overall environmental footprint.
International Standards for Life Cycle Analysis and Carbon Footprint Analysis
To ensure consistency and comparability of LCA and carbon footprint analysis, international standards have been established. These standards provide guidance on methodologies, data collection, and reporting practices. Some notable standards include:
ISO 14040 and ISO 14044
ISO 14040 and ISO 14044 as well as ISO14067, are international standards that provide guidelines for conducting LCA. These standards outline the principles, framework, and requirements for performing an LCA study. They ensure that LCA studies are conducted in a transparent, consistent, and scientifically robust manner.
GHG Protocol
The GHG Protocol is a widely recognized international standard for measuring and reporting greenhouse gas emissions. It provides guidance on calculating emissions from various sources, including direct emissions from operations, emissions from purchased electricity, and emissions from the supply chain. The GHG Protocol helps companies assess their carbon footprint and develop emission reduction strategies.
Driving Sustainability through Life Cycle Analysis and Carbon Footprint Analysis
Life Cycle Analysis and Carbon Footprint Analysis play a crucial role in driving sustainability and reducing environmental impact. By utilizing these tools, companies can:
Identify Hotspots and Prioritize Actions
LCA and carbon footprint analysis enable companies to identify environmental hotspots and prioritize actions for improvement. By understanding the areas with the highest environmental impact, companies can focus their efforts on implementing measures that will have the greatest environmental benefit.
Optimize Product Design and Development
LCA can be integrated into the product design and development process to create more sustainable products. By considering environmental factors from the early stages, companies can make informed decisions regarding material selection, energy efficiency, and waste reduction. This leads to the development of products that
Embracing Sustainability: A Call to Action
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and Carbon Footprint Analysis provide valuable insights into the environmental impact of products and processes. By utilizing these tools, companies can drive sustainability, reduce emissions, and create a more sustainable future. It is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers to embrace these practices and work together towards a greener world.
The Role of Businesses
Businesses play a crucial role in driving sustainability and reducing their environmental footprint. By integrating LCA and carbon footprint analysis into their practices, companies can:
Set Sustainability Goals
Setting sustainability goals based on LCA and carbon footprint analysis is a vital step for businesses. By establishing targets for reducing emissions, optimizing resource efficiency, and minimizing waste generation, companies can create a roadmap towards a more sustainable future.
Foster Innovation
Embracing LCA and carbon footprint analysis can inspire innovation within organizations. By evaluating the environmental impact of products and processes, companies can identify opportunities for improvement and drive innovation towards more sustainable alternatives. This can lead to the development of greener technologies, materials, and practices.
Collaborate with Suppliers and Stakeholders
Collaboration with suppliers and stakeholders is key to promoting sustainability throughout the value chain. By working together, companies can collectively reduce emissions, optimize resource usage, and implement sustainable practices. This collaboration can include sharing best practices, setting standards, and fostering transparency.
The Role of Consumers
Consumers also have a significant role to play in driving sustainability. By making informed choices and supporting sustainable products, consumers can:
Demand Transparency
Consumers can demand transparency from companies regarding their environmental impact. By seeking information on LCA and carbon footprint analysis, consumers can make more informed purchasing decisions and support companies that prioritize sustainability. This demand for transparency can encourage businesses to adopt more sustainable practices.
Support Sustainable Products
Choosing products with lower carbon footprints and considering their life cycle impact is a powerful way for consumers to contribute to sustainability. By supporting companies that prioritize sustainability, consumers can influence market trends and encourage the adoption of greener alternatives. This includes considering factors such as energy efficiency, recyclability, and eco-labels.
The Role of Policymakers
Policymakers play a critical role in driving sustainability by creating supportive frameworks and regulations. They can:
Promote Standardization
Policymakers can promote the standardization of LCA and carbon footprint analysis methodologies. By establishing consistent guidelines and reporting frameworks, policymakers facilitate comparability and transparency in environmental assessments.